An Ancient Near Eastern and Second Temple Reassessment of the “First Wife” Tradition – Lilith
The figure of Lilith has become one of the most widely discussed characters associated with the early chapters of Genesis, particularly in modern theological speculation and cultural interpretation. In some contemporary retellings, Lilith is portrayed as the first wife of Adam, created prior to Eve and departing the Garden of Eden following conflict with Adam. Yet the origins of this narrative lie far outside the canonical text of Genesis itself.
The present study examines the Lilith tradition through a historical and textual framework rooted in Ancient Near Eastern linguistics, Second Temple Jewish literature, and rabbinic interpretation. The primary aim is to determine whether the concept of Lilith as Adam’s first wife can be sustained through exegetical analysis of the biblical text or whether it emerges primarily through deductive interpretation imposed upon the text by later traditions.
While theological deduction is an unavoidable feature of interpretation—indeed all theological systems rely upon synthesis beyond the immediate words of Scripture—the Lilith tradition provides a compelling case study in the boundary between interpretive inference and post-biblical mythmaking. By tracing the development of Lilith from Mesopotamian demonology to medieval Jewish folklore, it becomes clear that the narrative of Lilith as Adam’s first wife is not grounded in the Genesis text itself but emerges from later interpretive traditions seeking to harmonize perceived tensions in the biblical narrative. Given this, is there still room to incorporate Lilith into the biblical narrative and remain faithful to biblical interpretation?

The Absence of Lilith in the Genesis Narrative
The canonical account of creation in Genesis offers no explicit reference to Lilith. The early chapters present two creation narratives that have often prompted interpretive discussion. Genesis 1:26–27 describes the creation of humanity (hāʾādām) in the image of God, stating that “male and female he created them.”¹ Genesis 2:18–23 then recounts the formation of the woman from the side of Adam within the Garden narrative.²
Some interpreters have proposed that these two passages imply the creation of two separate women, with Genesis 1 describing a primordial woman distinct from the Eve of Genesis 2.³ However, the majority of modern biblical scholarship understands Genesis 1 and Genesis 2 as complementary literary traditions within the Pentateuch rather than sequential historical events.⁴ I however, often challenge this view reading Genesis 1-2 as a sequential narrative reading or chronological reading of the text. If you read it this way, it may better open up the door for a first wife before Eve and the need for her to be “later” created.
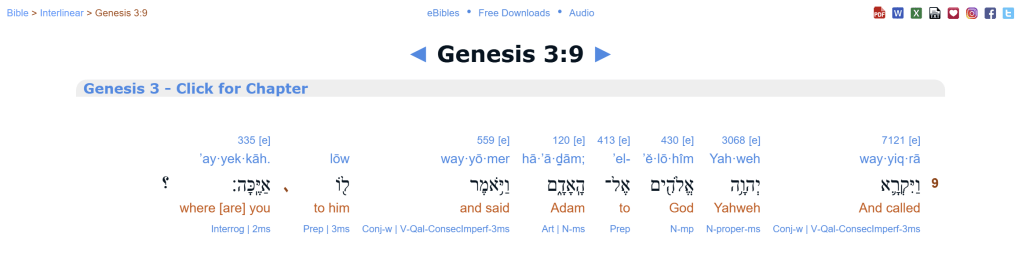
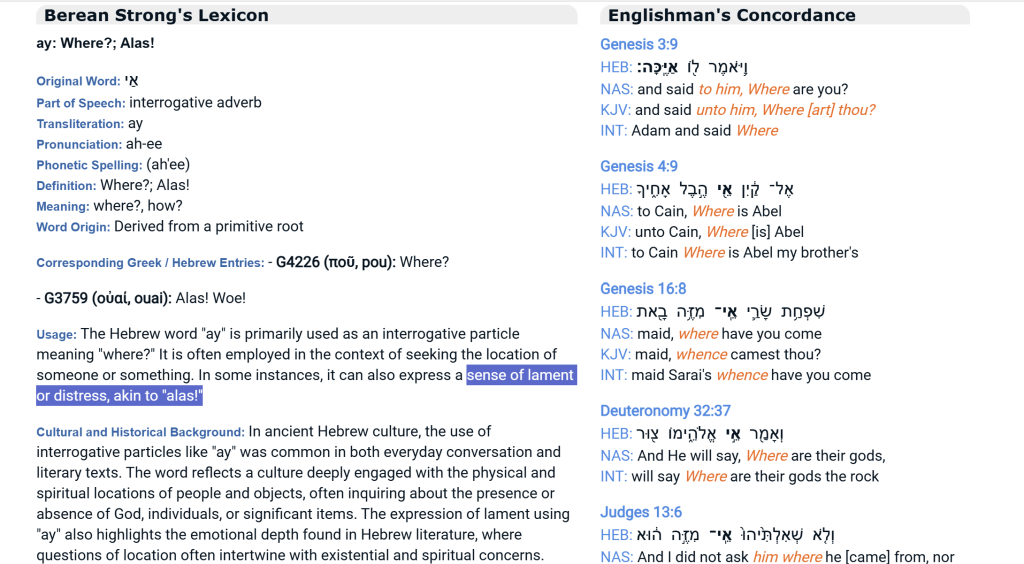
The only explicit appearance of the term לִילִית (lîlîṯ) within the Hebrew Bible occurs not in Genesis but in Isaiah 34:14, where the prophet describes the desolation of Edom and lists a series of wilderness creatures inhabiting the ruins.⁵ The term appears within a poetic catalogue of desert beings, including jackals and goat-demons (śeʿîrîm).⁶
Because the word appears only once in the Hebrew Bible, its meaning has long been debated. Some translations render it as “night creature” or “screech owl,” while others retain the transliteration “Lilith.”⁷ The context suggests a demonic or mythological wilderness being, rather than a historical figure associated with the Eden narrative.
In this light, a further feature of the Eden narrative that must be considered is the presence of mythopoetic and anthropomorphic imagery within the text itself. Several of the figures and elements within the primeval history are described in ways that blur the boundaries between natural creatures and symbolic agents within the narrative world. Gordon Wenham reminds us that the serpent in Genesis 3, for example, speaks and reasons in human language, engaging the woman in moral and theological dialogue despite being described as one of the “beasts of the field” (ḥayyat haśśādeh). Likewise, the cherubim placed at the entrance of Eden in Genesis 3:24 appear not as ordinary creatures but as composite guardian beings stationed at sacred space, paralleling protective figures associated with temple entrances throughout the Ancient Near East. Even the trees of the garden, particularly the Tree of Life and the Tree of the Knowledge of Good and Evil, function within the narrative as more than botanical objects, representing cosmic or moral realities embedded within sacred geography.
These features demonstrate that the Eden narrative employs a literary environment where symbolic and anthropomorphic elements are common. Animals converse, trees convey knowledge, and guardian beings protect the boundaries of sacred space. Such imagery resembles the mythopoetic storytelling common to the ancient world, where narrative symbolism communicates theological truths through figurative representation. Yet importantly, the text never introduces a figure resembling the later Lilith tradition within this symbolic cast of Edenic beings. If Genesis were intended to preserve a memory of such a character, one would reasonably expect some trace within the narrative alongside the serpent, the trees, and the cherubim. The absence of any such reference reinforces the conclusion that the Lilith tradition emerged not from the narrative structure of Genesis itself but from later interpretive speculation.
At the same time, it must be acknowledged that the biblical narrative frequently displays a remarkable economy of detail, often focusing narrowly on the theological point of the story being told while leaving many surrounding elements unexplained. The Scriptures regularly assume a broader narrative world that is only partially disclosed within any given passage. In numerous instances, later texts appear to illuminate or expand earlier material through retrospective inference, suggesting that not every element of the biblical worldview is exhaustively articulated at its first appearance. For example, the identity and role of the serpent in Genesis 3 remain largely undefined within the Eden narrative itself, yet later biblical literature associates the figure with cosmic opposition to God (cf. Rev. 12:9). Likewise, Genesis 6 briefly introduces the enigmatic “sons of God” and the Nephilim with minimal explanation, leaving subsequent Jewish traditions and later biblical reflections to wrestle with their meaning.
Note: Biblical interpretation frequently involves a degree of retrospective or “back-reading” into earlier texts, a hermeneutical practice widely recognized within both Jewish and Christian traditions. Later revelation often illuminates earlier passages in ways not immediately apparent in their original context. A well-known example is the Christian reading of the Old Testament through a Christological lens, where the life and work of Jesus are understood to fulfill and reveal deeper meanings within earlier Scriptures (e.g., Luke 24:27). Such interpretive movements demonstrate that retrospective theological inference can be legitimate, though it must remain anchored within the broader trajectory of the canonical text.
Lilith isn’t mentioned in the Genesis text and this narrative restraint may demonstrate that the biblical authors prioritize the theological thrust of the account rather than providing a comprehensive cosmology of every figure involved in the story. Consequently, while the absence of Lilith from the Genesis narrative strongly cautions against reading such a figure directly into the text, the broader pattern of Scripture also reminds interpreters that certain dimensions of the biblical world are occasionally clarified only through later reflection and textual development. The challenge for interpreters, therefore, is discerning the difference between legitimate theological inference grounded in later revelation and speculative deductions that extend beyond the trajectory of the canonical text.
Evidence from the Great Isaiah Scroll (1QIsaᵃ) discovered at Qumran further complicates interpretation. In this manuscript the term appears in plural form (liliyyôt), suggesting that the word may refer to a category of night spirits rather than a singular named entity.⁸ Thus, from the standpoint of textual criticism and lexical analysis, the Hebrew Bible provides no direct evidence that Lilith functioned as a character within the Genesis narrative.
Akkadian Linguistic Background and Ancient Near Eastern Demonology
The linguistic origins of the term lîlîṯ point toward a broader Ancient Near Eastern mythological context. In Akkadian texts, scholars have identified a group of supernatural beings known as lilu, lilītu, and ardat-lilî.⁹ These entities appear frequently in Mesopotamian incantation texts as malevolent wind or night spirits associated with illness, infertility, and sexual predation.¹⁰
The Akkadian līlû is commonly regarded as a loanword reflecting earlier Sumerian linguistic elements. The Hebrew lîlîṯ (Lilith) ultimately derives from the Sumerian root LIL, though most plausibly through the intermediary of Akkadian līlû and related demonological terminology rather than by direct borrowing from Sumerian.¹¹
Among the earliest literary references to a Lilith-like figure appears in the Sumerian narrative “Gilgamesh and the Huluppu Tree,” dating to the early second millennium BCE.¹² In this text a female being identified by the phrase ki-sikil-lil-la-ke inhabits the trunk of a sacred tree alongside a serpent and the Anzû bird until she is driven away by the hero Gilgamesh.¹³
Although the linguistic connection between this Sumerian phrase and the later Hebrew lîlîṯ remains debated, the narrative demonstrates the presence of female wind spirits in Mesopotamian mythology long before the composition of the Hebrew Bible.¹⁴
Archaeological evidence further attests to widespread belief in such spirits. Aramaic incantation bowls, dating between the fifth and seventh centuries CE, frequently contain protective formulas against Lilith and related demons.¹⁵ These bowls, often buried beneath homes, reflect a pervasive fear of nocturnal spirits believed to threaten women and infants.
Within this broader cultural environment, the reference to lîlîṯ in Isaiah likely reflects Israel’s awareness of Mesopotamian demonological traditions, particularly during the Babylonian exile.¹⁶ Yet the biblical authors do not develop these figures into elaborate mythological characters. Instead, the reference appears only as poetic imagery within a prophetic oracle of desolation.
Lilith in Second Temple and Dead Sea Scroll Literature
During the Second Temple period Jewish literature exhibits an increased interest in angelology and demonology. Within this context, Lilith appears as one among several destructive spirits.
The Dead Sea Scroll text Songs of the Sage (4Q510–511) contains an incantation intended to repel supernatural forces. Among the spirits mentioned are Lilith, the howling creatures, and desert demons.¹⁷
Similarly, other Second Temple texts reflect a worldview in which demonic forces inhabit the wilderness and threaten the righteous community.¹⁸ These references demonstrate that Lilith had become a recognized figure within Jewish demonology by the late Second Temple period.
Nevertheless, these texts still do not connect Lilith to Adam or the Eden narrative. Instead, Lilith appears alongside other supernatural beings associated with chaos and the desert.
This pattern aligns with the symbolic geography of the Hebrew Bible, where the wilderness frequently represents a realm of disorder and demonic presence, standing in contrast to the ordered sacred space of the temple.¹⁹
Thus, in Second Temple literature Lilith functions as one among many hostile spirits, rather than a primordial human figure.
Rabbinic Tradition and the Emergence of the “First Wife” Narrative
The identification of Lilith as Adam’s first wife appears only in medieval Jewish literature. The earliest known source is the Alphabet of Ben Sira, a satirical work composed sometime between the eighth and tenth centuries CE.²⁰
In this narrative Lilith is said to have been created from the earth just as Adam was. When Adam demands sexual submission, Lilith refuses, declaring that both were created equally from the ground.²¹ She then pronounces the divine name and flees the Garden of Eden.
The story continues by describing Lilith as a demonic figure who preys upon newborn children, reflecting earlier traditions associated with infant mortality.²²
Many scholars interpret the story as a midrashic attempt to resolve the apparent tension between Genesis 1 and Genesis 2.²³ If Genesis 1 describes the simultaneous creation of male and female, some interpreters speculated that this might refer to a woman preceding Eve.
Yet even within Jewish tradition the Lilith myth was not universally accepted. Rationalist thinkers such as Maimonides regarded many demonological traditions as remnants of ancient superstition rather than theological doctrine.²⁴
Thus the identification of Lilith as Adam’s first wife represents a late interpretive development, emerging more than two millennia after the composition of Genesis.
Note: The fact that a theological idea emerges later in the history of interpretation does not automatically invalidate it as a subject of serious consideration. Many theological systems developed long after the biblical texts themselves were written. For example, the systematic framework of Reformed theology was largely articulated in the sixteenth and seventeenth centuries, yet it remains widely studied and engaged by biblical scholars today. Historical development alone, therefore, is not sufficient grounds to dismiss an interpretive proposal; the question must ultimately be whether the idea can be responsibly grounded within the broader trajectory of the biblical witness.
Deduction and the Boundaries of Exegetical Interpretation
The Lilith tradition ultimately illustrates a significant hermeneutical issue within biblical interpretation: the distinction between textual exegesis and theological deduction.
Interpretation necessarily involves drawing conclusions that extend beyond the explicit wording of a text. Indeed, the construction of systematic theology depends upon synthesizing diverse biblical passages into coherent doctrinal frameworks.²⁵
However, responsible interpretation requires that such deductions remain grounded in the historical and literary context of the text itself. When interpretive conclusions depend primarily upon later traditions rather than the biblical narrative, the risk arises that extrabiblical mythology may be read back into Scripture.²⁶
The Lilith tradition exemplifies this process. The theory that Lilith was Adam’s first wife relies upon several deductive steps:
- The assumption that Genesis 1 and Genesis 2 describe two separate creations of women.
- The identification of the “night creature” in Isaiah 34 with a personal demonic figure.
- The incorporation of Mesopotamian demonology into the Genesis narrative.
None of these steps arise directly from the text of Genesis itself. Rather, they reflect later interpretive speculation layered upon the biblical narrative.²⁷
Consequently, while the Lilith tradition remains historically fascinating, most scholars have then deduced that it cannot be considered a faithful exegetical reading of the Genesis account… but not all of them!
Conclusion
The development of the Lilith tradition demonstrates how biblical interpretation evolves through the interaction of language, culture, and theological imagination. Linguistic evidence connects the Hebrew lîlîṯ with a broader family of Ancient Near Eastern night spirits, while Second Temple literature confirms that Lilith functioned within Jewish demonology as one among many destructive beings.
Only in the medieval period did interpreters reinterpret this figure as Adam’s first wife in an effort to harmonize perceived tensions in the Genesis creation narratives.
While such deductions may hold cultural or literary interest, they remain extrinsic to the biblical text itself. The Genesis narrative consistently portrays Adam and Eve as the primordial human pair, and the Lilith legend represents a later tradition rather than an exegetical conclusion.
In this sense, the Lilith tradition provides a cautionary example within biblical interpretation: deduction may enrich theological reflection, but when it moves too far beyond the textual foundations of Scripture it risks transforming interpretation into mythology.
Acknowledgment: The author gratefully acknowledges Dr. Mark Chavalas for his assistance and expertise in matters relating to Akkadian philology.

Footnotes
- Genesis 1:26–27.
- Genesis 2:18–23.
- Raphael Patai, The Hebrew Goddess (Detroit: Wayne State University Press, 1990), 221.
- Gordon Wenham, Genesis 1–15 (Word Biblical Commentary; Dallas: Word, 1987), 5–7.
- Isaiah 34:14.
- John Oswalt, The Book of Isaiah 1–39 (NICOT; Grand Rapids: Eerdmans, 1986), 624.
- Michael Heiser, The Unseen Realm (Bellingham: Lexham, 2015), 188.
- Eugene Ulrich, The Dead Sea Scrolls and the Origins of the Bible (Grand Rapids: Eerdmans, 1999), 79.
- Samuel Noah Kramer, History Begins at Sumer (Philadelphia: University of Pennsylvania Press, 1981), 188.
- Tzvi Abusch, “Mesopotamian Witchcraft,” Journal of Near Eastern Studies 48 (1989): 3–7.
- Dictionary of Deities and Demons, ‘lillith’ by M. Hutter, pp. 520-521.
- Samuel Noah Kramer, “Gilgamesh and the Huluppu Tree,” Assyriological Studies 10 (1938): 1–30.
- Ibid., 12–15.
- Tikva Frymer-Kensky, In the Wake of the Goddesses (New York: Free Press, 1992), 36–37.
- James Montgomery, Aramaic Incantation Texts from Nippur (Philadelphia: University of Pennsylvania Press, 1913), 112.
- Mark Smith, The Origins of Biblical Monotheism (Oxford: Oxford University Press, 2001), 148.
- 4Q510–511, Songs of the Sage.
- Loren Stuckenbruck, The Myth of Rebellious Angels (Tübingen: Mohr Siebeck, 1997), 202.
- John Walton, The Lost World of Genesis One (Downers Grove: IVP Academic, 2009), 72.
- Alphabet of Ben Sira, ed. David Stern (New Haven: Yale University Press, 2011), 89.
- Ibid., 90.
- Raphael Patai, The Hebrew Goddess, 225.
- Judith Baskin, Midrashic Women (Hanover: Brandeis University Press, 2002), 34.
- Maimonides, Guide for the Perplexed III.37.
- Kevin Vanhoozer, The Drama of Doctrine (Louisville: Westminster John Knox, 2005), 87.
- Brevard Childs, Introduction to the Old Testament as Scripture (Philadelphia: Fortress, 1979), 36.
- John Day, Yahweh and the Gods and Goddesses of Canaan (Sheffield: Sheffield Academic Press, 2002), 129–130.
Bibliography for Further Reading
Primary Sources and Ancient Texts
Abusch, Tzvi, and Daniel Schwemer. Corpus of Mesopotamian Anti-Witchcraft Rituals. Leiden: Brill, 2011.
Alexander, Philip S. The Dead Sea Scrolls: Hebrew, Aramaic, and Greek Texts with English Translations. Tübingen: Mohr Siebeck, 1994.
Charlesworth, James H., ed. The Old Testament Pseudepigrapha. 2 vols. New York: Doubleday, 1983–1985.
Kramer, Samuel Noah. History Begins at Sumer. Philadelphia: University of Pennsylvania Press, 1981.
Kramer, Samuel Noah. “Gilgamesh and the Huluppu Tree.” In Assyriological Studies, vol. 10. Chicago: University of Chicago Press, 1938.
Montgomery, James A. Aramaic Incantation Texts from Nippur. Philadelphia: University of Pennsylvania Press, 1913.
Ulrich, Eugene. The Dead Sea Scrolls and the Origins of the Bible. Grand Rapids: Eerdmans, 1999.
Ancient Near Eastern Religion and Demonology
Black, Jeremy, and Anthony Green. Gods, Demons, and Symbols of Ancient Mesopotamia. Austin: University of Texas Press, 1992.
Bottéro, Jean. Religion in Ancient Mesopotamia. Chicago: University of Chicago Press, 2001.
Frymer-Kensky, Tikva. In the Wake of the Goddesses: Women, Culture, and the Biblical Transformation of Pagan Myth. New York: Free Press, 1992.
Jacobsen, Thorkild. The Treasures of Darkness: A History of Mesopotamian Religion. New Haven: Yale University Press, 1976.
Leick, Gwendolyn. Mesopotamia: The Invention of the City. London: Penguin, 2002.
Second Temple Jewish Literature and Demonology
Collins, John J. The Apocalyptic Imagination. Grand Rapids: Eerdmans, 2016.
Stuckenbruck, Loren T. The Myth of Rebellious Angels: Studies in Second Temple Judaism and New Testament Texts. Tübingen: Mohr Siebeck, 1997.
VanderKam, James C. An Introduction to Early Judaism. Grand Rapids: Eerdmans, 2001.
Wise, Michael, Martin Abegg, and Edward Cook. The Dead Sea Scrolls: A New Translation. San Francisco: HarperCollins, 2005.
Rabbinic Literature and the Lilith Tradition
Baskin, Judith R. Midrashic Women: Formations of the Feminine in Rabbinic Literature. Hanover: Brandeis University Press, 2002.
Patai, Raphael. The Hebrew Goddess. 3rd ed. Detroit: Wayne State University Press, 1990.
Stern, David. The Alphabet of Ben Sira: A Critical Edition and Commentary. New Haven: Yale University Press, 2011.
Trachtenberg, Joshua. Jewish Magic and Superstition. Philadelphia: University of Pennsylvania Press, 1939.
Genesis, Creation Narratives, and Ancient Near Eastern Context
Day, John. Yahweh and the Gods and Goddesses of Canaan. Sheffield: Sheffield Academic Press, 2002.
Heiser, Michael S. The Unseen Realm: Recovering the Supernatural Worldview of the Bible. Bellingham: Lexham Press, 2015.
Sarna, Nahum. Genesis. JPS Torah Commentary. Philadelphia: Jewish Publication Society, 1989.
Walton, John H. Ancient Near Eastern Thought and the Old Testament. Grand Rapids: Baker Academic, 2006.
Walton, John H. The Lost World of Genesis One. Downers Grove: IVP Academic, 2009.
Wenham, Gordon J. Genesis 1–15. Word Biblical Commentary. Dallas: Word Books, 1987.
Westermann, Claus. Genesis 1–11: A Commentary. Minneapolis: Fortress Press, 1994.
Hermeneutics and Biblical Interpretation
Childs, Brevard S. Introduction to the Old Testament as Scripture. Philadelphia: Fortress Press, 1979.
Vanhoozer, Kevin J. The Drama of Doctrine. Louisville: Westminster John Knox Press, 2005.
Wright, N. T. Scripture and the Authority of God. New York: HarperOne, 2013.